William Henry Quilliam Was Born on 10th April 1856 to a Wealthy Family in Liverpool
The Victorian era of the United Kingdom and its overseas Empire spans the 63-twelvemonth reign of Queen Victoria (1837-1901). By this time, the role of the monarch was to reign, rather than dominion. Victoria served every bit figurehead for the nation.
The menstruum saw the British Empire grow to go the first global industrial power, producing much of the earth's coal, iron, steel and textiles. The Victorian era saw revolutionary breakthroughs in the arts and sciences, which shaped the world as we know it today.
These transformations led to many social changes with the birth and spread of political movements, most notably socialism, liberalism and organised feminism.
Timeline of the Victorian Empire
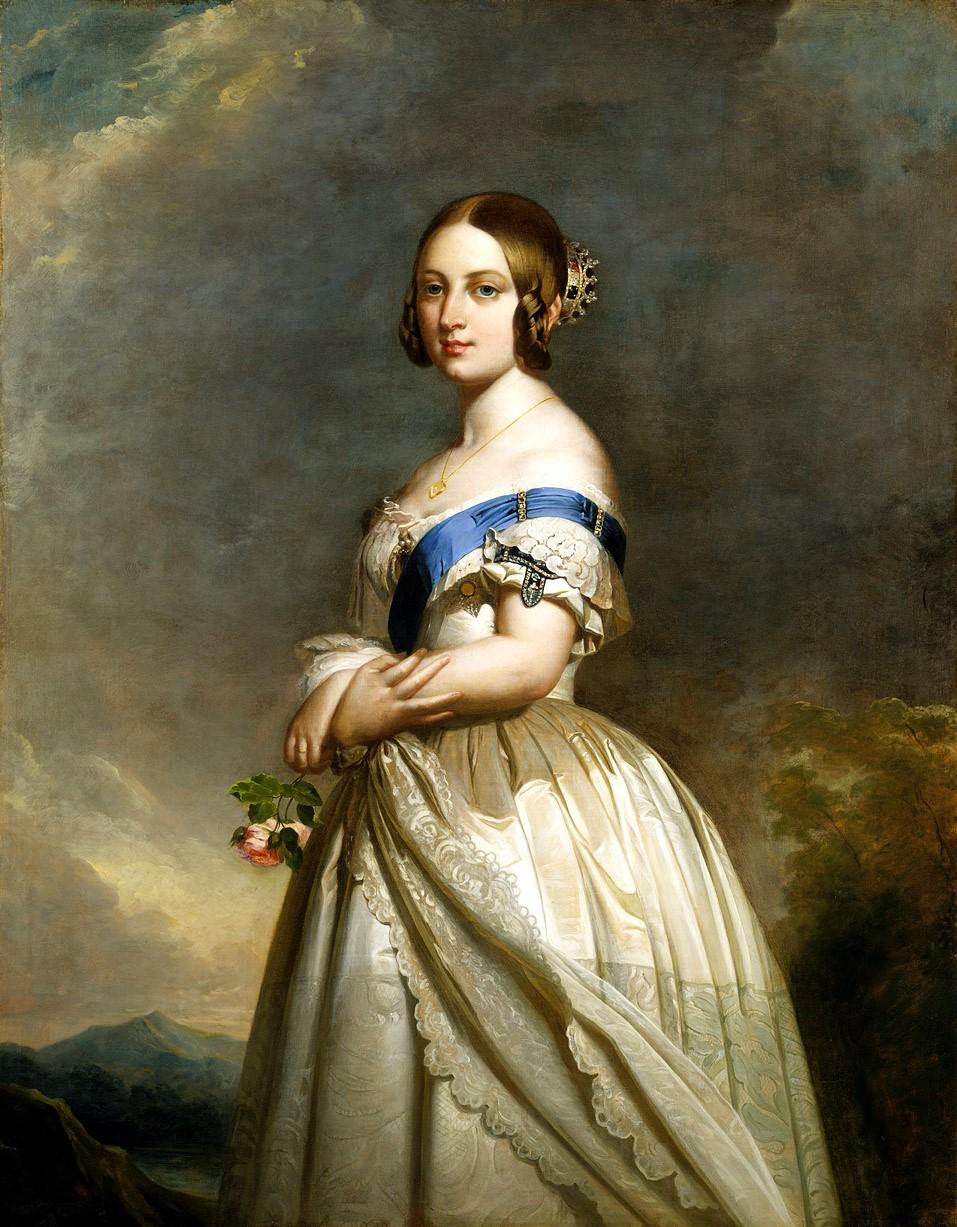
24 May 1819 | Victoria is born
Born at Kensington Palace and christened Alexandrina Victoria, the babe princess took her place equally a potential heir to the throne.
twenty June 1837 | Victoria ascends to the throne
After the death of King William IV on 20 June 1837, his 18-twelvemonth-old niece was given the title the Queen of England. She became heir to the throne as her three uncles ahead of her in the line of succession - George Iv, Frederick Duke of York, and William 4 - had no legitimate children who survived.
The coronation ceremony took place on the 28 June and was held in Westminster Abbey later a procession through the streets from Buckingham Palace. It is thought over 400,000 visitors arrived for the coronation.
1 August 1838 | Slavery abolished in the British Empire
While slavery was abolished in the British Empire on i Baronial 1834, merely children under the age of six were freed immediately under the terms of the 1833 Emancipation Act.
All other former slaves were bound every bit 'apprentices,' where they connected to work without pay for their quondam owners. When the apprenticeship menstruum ended in 1838, over 700,000 slaves were freed in the British Caribbean. Plantation owners received nearly £20 one thousand thousand in government bounty for the loss of their slaves. The old slaves received nothing.
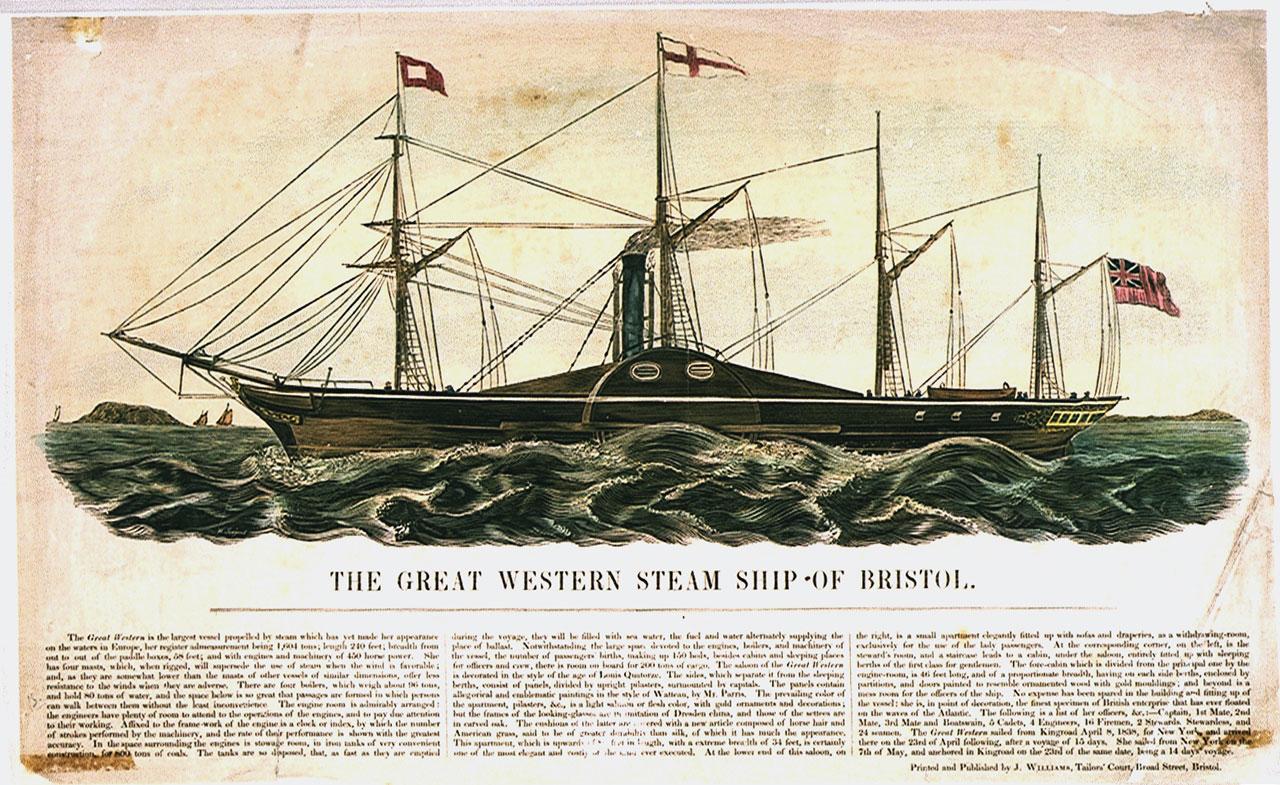
31 March 1838 | SS Not bad Western makes its maiden voyage
The SS Dandy Western was the first ship designed past Isambard Kingdom Brunel (1806 - 1859). At the time of construction, The SS Great Western was the longest steamship in the globe, built with the express purpose of crossing the Atlantic. The ship made a maiden voyage from Avonmouth in Bristol to New York in nether 15 days, becoming the fastest transatlantic crossing in each management.
17 September 1838 | London to Birmingham line opens
The London to Birmingham Railway was one of the largest technology projects attempted in the world. First proposed in the early 1830s to connect the capital with the booming cities of Manchester and Liverpool, the railway became London's first rail line (with a station in Euston). The 112 miles between London Euston and Birmingham Curzon Street took a journeying time of 12 hours and 30 minutes.
The experience gained from the railway formed the foundations of ceremonious engineering in Britain and established the construction technology of the railway age.
10 January 1840 | The 'penny mail service' implemented
Introduced by Rowland Hill, the Penny postal arrangement revolutionised communications in the UK. Before the Penny Post, messages were paid for past the recipient. The loftier costs were sometimes equally much equally a day's wages, causing many recipients to pass up their messages.
The Penny postal arrangement was uncomplicated. Anyone could send a letter to anywhere within the UK for a penny. This new method was attainable for both the wealthy and the poor and significantly improved the advice of Uk. In 1839, 76 meg letters were posted in the United kingdom. By 1849, this amount had doubled to 347 meg messages.
ten February 1840 | Queen Victoria marries Prince Albert
At the age of 21, Victoria married her cousin, Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, a High german Prince at the Chapel Royal in St. James's Palace. Over the years of their marriage, Victoria had nine children, many of who married into other royal families in Europe.
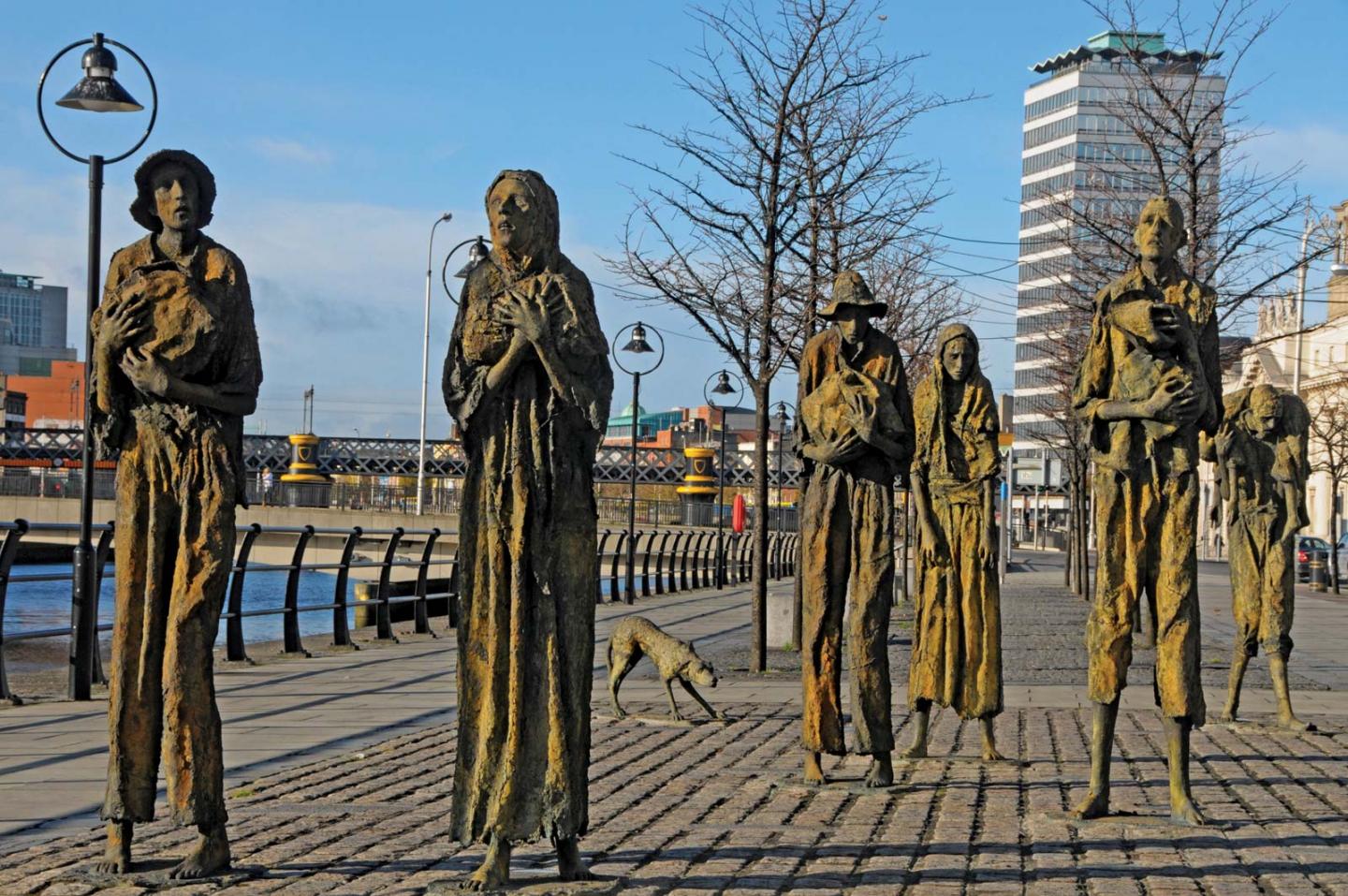
September 1845 | Irish gaelic potato famine begins
In 1845, Ireland'due south potato crop was destroyed by infestation with the fungal illness known as irish potato blight. The disease rotted the potatoes in the basis, ruining the master food source for millions of people. The blight lasted for another four years, causing illness and mass starvation beyond Ireland and killing a million people out of a population of eight 1000000.
Many Irish labourers and farmers worked on estates owned by British landlords. Following the blight, the tenants were expected to still pay rent despite having no income from their crops. This prompted the eviction of over a quarter of a one thousand thousand people betwixt 1845 and 1854 and led to the mass migration of a one thousand thousand people, looking to start a new life abroad – many of them in America.
July 1848 | Public health act passed
Following a astringent cholera outbreak across the world, killing xiii,000 people, social reformer Edwin Chadwick was commissioned to observe ways of improving disease prevention and sanitary weather condition in Britain. This study led to the creation of the Public Health Act of 1848, legislation that placed the supply and treatment of water and waste product under single local government who could enhance funds for improvements to tackle unsanitary conditions.
1 May 1851 | The Great Exhibition opens
The Great Exhibition was the start of a series of World's Fairs - an international exhibition showcasing the achievements of nations, and present the latest discoveries in science and technology.
The prove took place in a temporary built structure, known every bit the Crystal Palace in Hyde Park, London, from 1 May to 15 October. The show proved hugely popular beyond the world, attracting over six million visitors over five months - the equivalent to a tertiary of the entire population of Britain at the time.
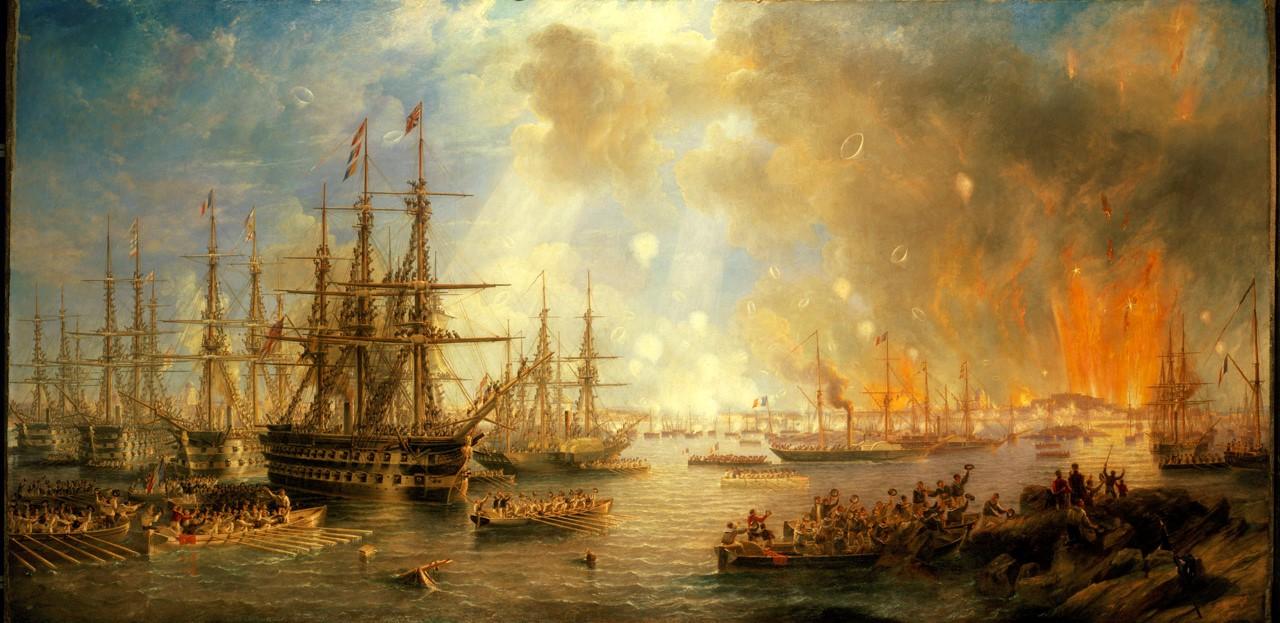
28 March 1854 | Crimean war begins
The Crimean War was a conflict between the Russian Empire and an brotherhood of French, British, Ottoman (or the Turkish Empire) and Sardinian troops. The war broke out in the autumn of 1853 with Britain and French republic declaring war on Russia in 1854.
The main intention of the British, French and Ottoman alliance was to hinder Russian expansion into the Turkish empire. Religious tensions likewise played a part with Russia taking issue that the holiest sites in Christianity, such as Jerusalem and Bethlehem, remained under Turkish Muslim control.
The war came to a determination in February 1856 with the Treaty of Paris with the role-give up of Russia. The war resulted in a massive death toll on both sides. A full of 1.five one thousand thousand total soldiers fought in the Crimea War with over 367,000 dying.
24 August 1856 | Henry Bessemer develops a new process for manufacturing steel
Historically, steel proved very costly to produce and could only be used for the manufacture of modest, valuable items, such as knives, swords and armour. In 1856, Henry Bessemer discovered a method of converting atomic number 26 into steel, which was both stronger and lighter. This production technique became known as the Bessemer Converter. The process revolutionised the construction industries, enabling Britain to build large-scale structures such as bridges, trains and boats.
x May 1857 | Outbreak of mutiny in Bharat
In 1857, Bengal Light Cavalry soldiers rebelled against their British commanders. The news of the mutiny spread across India and over the course of the twelvemonth, caused a serial of similar outbreaks across the subcontinent.
Many Indians rose against the British; however, many others also fought for the British, and the bulk remained seemingly compliant to British dominion. The rebellion continued until a rebel defeat in June 1858 at the city of Gwalior and the signing of a peace treaty in July. Notwithstanding, after the peace treaty, there were repercussions as British forces brutally suppressed whatever further attempts at defection.
The uprising was the largest threat to Uk's colonial rule of the Indian subcontinent. This violent struggle led to the dismantling of the East India Company, placing India under the dominion of the British government. Communications too improved with government and legislative councils now containing an Indian-nominated chemical element. For many Indians, the wildcat marked the beginning of their long struggle for independence.
24 November 1859 | On the Origin of Species published
The foundation of evolutionary theory, On the Origin of Species, was published by Charles Darwin (12 Feb 1809 - xix April 1882), a leading British biologist and naturalist. On publication, the book sold out immediately. The volume became an international best-seller, but opinion on the arguments for evolution and natural pick remained fiercely divided throughout Darwin'south life.
fourteen Dec 1861 | Prince Albert dies.
At the age of 42, Prince Albert died. Many historians believe the cause of expiry to exist typhoid, a affliction found in contaminated water. Filled with grief, Queen Victoria chose not to make a public appearance for x years until afterwards his decease. She commissioned several monuments in his honour, including the Purple Albert Memorial in Kensington Gardens, completed in 1876.
9 January 1863 | Opening of the London Cloak-and-dagger
The world's first hush-hush railway, the Metropolitan Railway opened in London running 6 km between Paddington Station and Farringdon Street. Within the showtime year, 9.5 million passengers were carried, in the 2nd year, this increased to 12 million. It took another 21 years (from 1863 to 1884) to consummate the Inner Circle of tube lines in central London. The railway system was operated past steam trains until its electrification in 1890.
eighteen October 1871 | Death of Charles Babbage, creator of the modern estimator
Charles Babbage (1791 – 1871) was a mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer. He is seen as "the father of the calculator" due to his designs of the Analytical Engine. He died at the age of 79. Half of Babbage'south brain is preserved at the Hunterian Museum at the Imperial College of Surgeons in London; the other one-half is on display in the Science Museum in London.
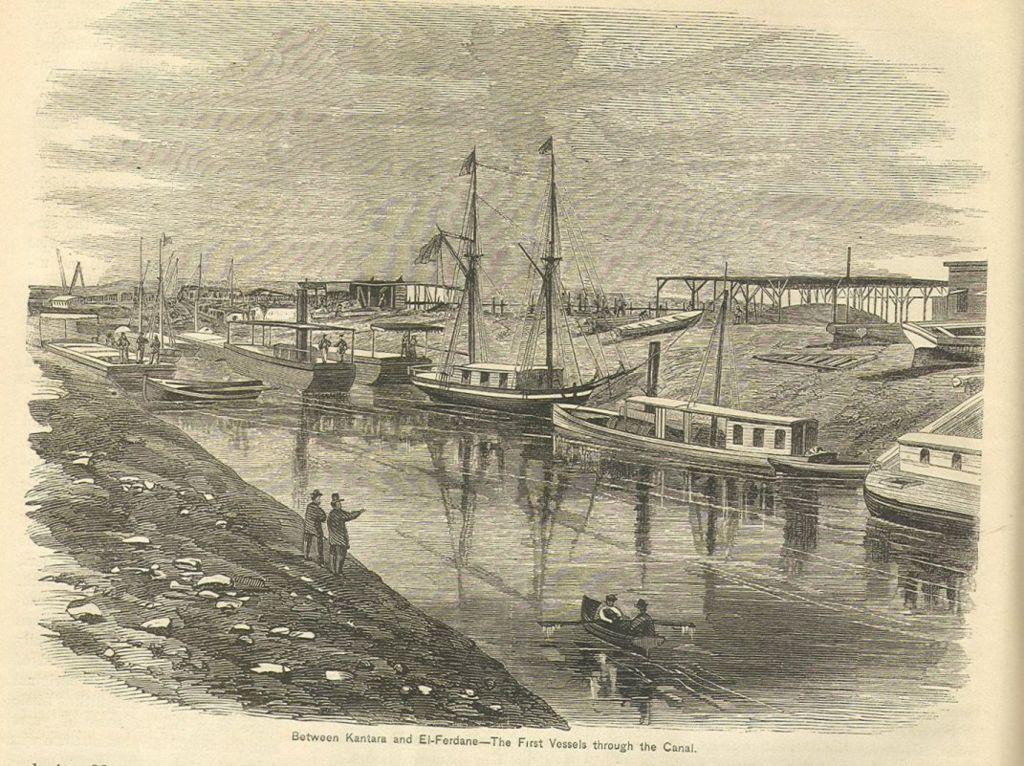
17 November 1869 | The Suez Culvert Opens
The Suez Culvert, a 100-mile waterway in Egypt that connects the Mediterranean and Red Seas was opened to improve trade links with India, S East asia and the Far E. Constructed past the French business, the Suez Culvert Visitor between 1859 and 1869, the canal opened initially under French command, which was then shared with the British.
March 1876 | Alexander Graham Bong patents the telephone
In March, 29-year-old Scotsman, Alexander Graham Bell received a patent for his revolutionary new invention, the telephone. Iii days after filing the patent, Bell spoke the start intelligible message into the telephone, saying to his assistant, "Mr Watson, come hither, I demand you."
two August 1880 | Education compulsory for children under 10
The Uncomplicated Education Act 1880 was a policy which made school attendance mandatory from ages 5 to 10. Introduced by social reformer and member of the liberal party, A.J. Mundella, the instruction neb quietly overrode the Factory Acts, dramatically reducing the corporeality of time young children were allowed to spend in mill and manufacturing plant piece of work.
25 July 1889 | Founding of the Women'due south Franchise League
Emmeline Pankhurst, the British women'due south rights activist, founded the Women's Franchise League, a political system that campaigned to allow women the correct to vote in local elections. The success of mobilising this campaign group led to the creation of the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) in 1903 and the rise of the suffragette movement.
22 January 1901 | Queen Victoria dies
Queen Victoria died later on a period of poor wellness at the age of 81. Her son and her eldest grandson were both at her bedside. Her 63-year reign was, at the time, the longest in British history (now surpassed by Elizabeth Two) and had seen the growth of an empire. She was succeeded by her son, Prince Albert Edward Wettin, who took the throne every bit Male monarch Edward 7.
Source: https://www.rmg.co.uk/stories/topics/what-happened-during-victorian-era








0 Response to "William Henry Quilliam Was Born on 10th April 1856 to a Wealthy Family in Liverpool"
Post a Comment